In the history of man, the present 'urban man' has moved away from nature and animals to the farthest edge. Running away from this little by little every day. Let's talk about Dhaka city, how many different animals can be seen walking from one end of this city to the other? Are there too many animals outside the human race to survive in this city? Or are there plants?
In cities around the world, the nature of life has been trimmed with the predominance of human convenience. In our present world, the definition of a city has established the idea that animals can only be seen in zoos, elsewhere they are a nuisance. As a result, even in the villages where urbanization is taking place, individual ecosystems are being evicted freely. But this city isolated from nature is giving rise to various problems. Its residents are unknowingly suffering from various problems. Food, water levels of chemicals are rising, the city is overheated and people are dying prematurely due to air pollution. Man therefore has to rebuild his cities in a new way, conserving biodiversity and adapting to nature.
How is the idea of the city changing?
Rural areas are declining in developing countries. As a result of rapid urbanization, the size of the city is increasing. The city is just a place for people to live, this idea is being established in the minds of the people. From the advertisement of building a new city to the planning table, the nature of life is being avoided as much as possible. The idea that there will be only people in the city, mostly pets, is slowly gaining ground in developing countries.
As a result, the damage to the ecosystem established in the area is being avoided directly when building new cities, or bringing people-centered development to the fore. If a railway line or a coal power plant is built in an area, the people of that area are being considered, the loss of human life in its sound or vibration is being considered. But birds, trees, insects and squirrels in the same ecosystem are easily avoided. But if this situation continues, there will be nothing left in the next twenty to twenty-five years in the developing countries, which are the source of biodiversity in the world.
The way death is becoming
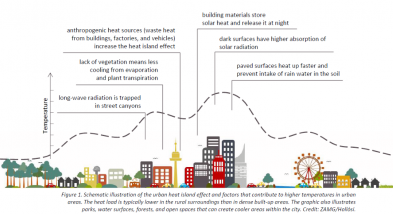
As a result of development with priority given to human convenience, people are already facing various problems in cities all over the world. One of the major aspects of this is the unexpected rise in temperature in the city. According to the United States to say , in urban areas, due to an unexpected increase in temperature due to climate mrtyujhuki mrtyujhukira more than any other. Infrastructure built with a rod of cement is becoming much hotter than a city field or empty space . Also, cities do not have adequate water bodies, cities around the world are prone to fires from late spring to mid-summer, and human casualties are on the rise. There is also air pollution, according to the World Health Organization, 6 million people worldwide die every year as a direct or indirect result of air pollution.
Organic waste management is a major infrastructural problem in the major cities of the world. Developed countries are already trying to process waste in other ways, including power generation from waste. In developing countries, however, the process is largely cumbersome, with waste being transferred from one area to another, and efforts being made to keep the city clean by dumping waste somewhere outside the city. Added to this is another problem of polythene and plastic. Accumulated on land or in the sea, it is damaging the ecosystem, the entire food chain.
But in the long history of human beings, animals, birds were the consumers of everything that was thrown away in the form of waste. Animals have been left out as much as we have started to make the city eights and human-centered, especially the excessive use of chemicals in food is damaging the relationships between the food chains in nature. The waste we dump in this ecosystem is harmful to the animal as a result of the use of harmful chemicals for food. The biggest victims are those in our ecosystem who pick up dead animals or organic food, which we identify as 'scavengers'.

One of them is vultures, vultures have decreased in the country after the use of 'Diclofenac' and 'Ketoprofen' as an analgesic for cattle increased. Because this chemical can cripple the vulture's kidneys. The drug was given to treat the dead animal in its lifetime, its indirect effect being the extinction of vultures. At present, the use of this drug in cattle is banned in different countries of the world including Bangladesh.
What to do next?
In the reality of a developing country, there has been a long-running debate about how much development is possible by protecting life, nature and the ecosystem. Developed countries are already listing the biodiversity in cities , trying to shape the city accordingly.
This is a process of 'pranibaicitrya sensitive urban planning, "he said in English is ' Biodiversity-Sensitive Urban Design (BSUD )'. Here the city is arranged keeping in mind the importance of every animal in an ecosystem except human beings. First, a city will protect the ecosystem of every animal in it. Britain's Royal Society for the Protection of Birds has already demanded a law called the Nature and Wellbeing Act . The importance of nature in protecting the physical and mental health of the people has been raised, and efforts have been made to preserve it by law.
It is very difficult to get direct results of investing in nature conservation, but developed countries have started investing in urban nature conservation with far-reaching thinking in mind. One of the reasons for this is that the developed countries of the world have come to understand the new problems of the city in this century. One of them is that our behavior in the city has destroyed the way most animals live. Forced them to leave their place. A small example of this is the free application of pesticides.
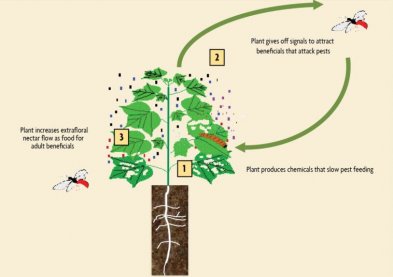
Studies have shown that when an insect first attacks a tomato plant, the plant itself responds to it with its own defenses, making chemicals in the leaves, and the chemical is released into the air from the insect's thorny parts. When this chemical message reaches the tree next to it, it also makes its own 'insect repellent' chemical, meaning that insects cannot attack more than one or two trees, in the meantime most trees become alert. It also survives insects, as well as trees. There is a relationship between the two. No one is lost from nature. Again, birds survive by relying on insects. The pesticide has an indirect effect on it, the number of birds decreases and in fact its effect on pollination.
Yet naturally wild tomatoes (Solanumn pennellii) are found in various parts of the Atacama Desert in Peru. Researchers there have found that when an insect attacks a tomato tree, the word of the attack reaches another tomato tree through the network of another tree. This protection is not just airborne , the plant has a complex communication system under the ground, called a microrizal network. Through this, if a tree is attacked for any reason, its message reaches the surroundings. But modern farming has destroyed all levels of the natural defense system.
However, advanced and hybrid varieties have been invented to maximize our benefits. Pruning has been done many times to increase production. Many species of hybrids have increased their attack due to weakened immune systems. The chemical pesticides on the market are killing the insects that attack the crops as well as the insects that are needed for the ecosystem. Insects useful in pollination are having a detrimental effect on bees. The most frightening thing is that pesticides are entering our food chain directly.
Has man been able to subdue nature?
One manifestation of man's power is that he has been able to control his nature, to bring everything around him to his advantage. For a long time people have done this in agriculture, in industry, they have cultivated for miles and miles, they have destroyed the surrounding reservoirs, the vegetation to increase the yield, they have overused the source of ground water. It has increased yields, started meeting human needs, but over time valuable varieties have been lost in this production process, diversity has decreased. The soil, air has been polluted, heavy metals and chemicals have entered the overproduced material. As a result, food, water, soil or air are not safe.
Suddenly people may not be able to get out of this situation. It is not possible to make cities animal friendly in a matter of moments, nor is it possible to reduce hazardous chemicals in agriculture or industry. But in the long run, this is the biggest challenge for human survival.

So the world is looking for a way to use the current scientific research to produce the least damage to nature. It is more important to be united than to be able to control the environment, and this requires a long-term plan to integrate the environment and biodiversity with humans. In the future, the biggest challenge for human beings in this world is to survive with biodiversity and nature.

